QXMD
A scalable parallel software for quantum molecular dynamics (QMD) with various extensions (X), where X currently supported include adiabatic and non-adiabatic (NA). QMD follows the trajectories of all atoms, while interatomic forces are computed quantum mechanically based on density functional theory (DFT) with a plane-wave basis and pseudopotential formalism. NAQMD describes electronic excitations using the linear-response time-dependent DFT (LR-TDDFT). Transitions between excited electronic states are treated using surface hopping algorithm. Photo-excitation is described as a non-adiabatic process that involves electronic transitions and coupled nuclear motion.
QXMD Software Repository
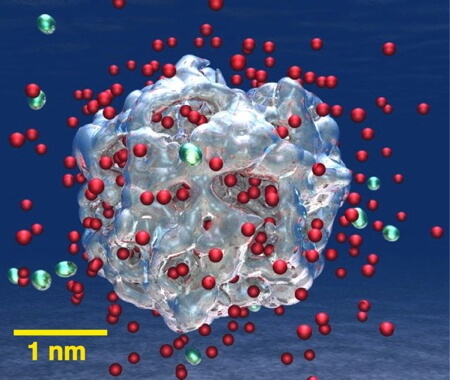
16,611-atom QMD simulation on 786,432 IBM Blue Gene/Q cores to study on-demand hydrogen production from water using LiAl particles.
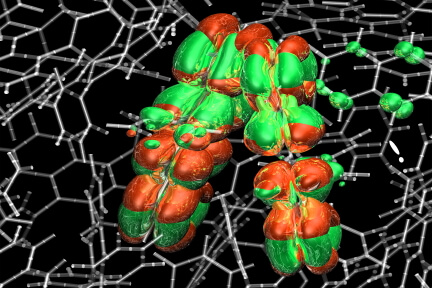
6,400-atom DCR-NAQMD simulation to study photoexcitated electron-hole pairs in organic solar cells.
References
- A divide-conquer-recombine algorithmic paradigm for large spatiotemporal quantum molecular dynamics simulations, F. Shimojo, R. K. Kalia, M. Kunaseth, A. Nakano, K. Nomura, S. Ohmura, K. Shimamura and P. Vashishta, Journal of Chemical Physics 140, 18A529 (2014).
- Quantum molecular dynamics in the post-petaflop/s era, N. A. Romero, A. Nakano, K. Riley, F. Shimojo, R. K. Kalia, P. Vashishta, and P. C. Messina, IEEE Computer 48(11), 33 (2015).
Published on May 17th, 2017
Last updated on January 27th, 2020

